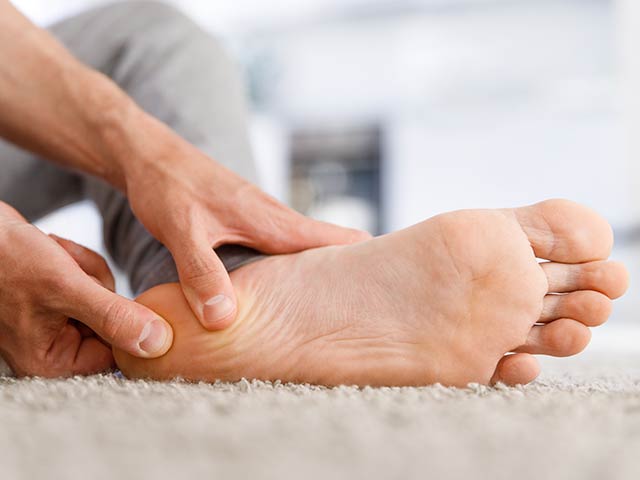
Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a painful foot ailment that can interfere with daily activities and lead to long-term discomfort if left untreated. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis of plantar fasciitis, offering valuable insights to help you understand this condition better.
Introduction
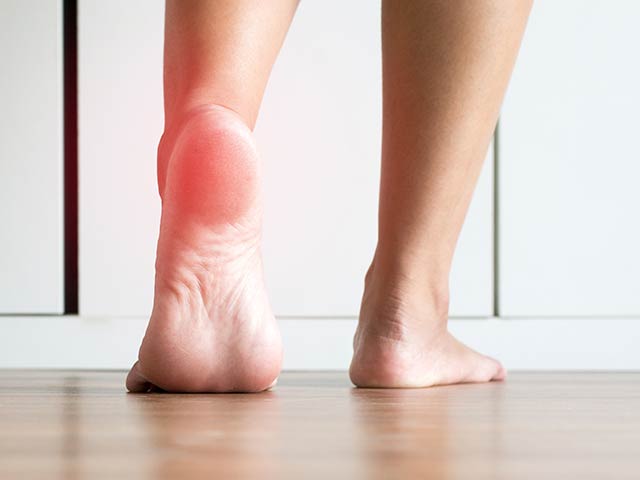
Plantar fasciitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs along the bottom of your foot, connecting your heel bone to your toes. This condition typically develops gradually and can affect anyone, but it is more common in individuals who spend long hours on their feet or engage in high-impact activities.
Causes of Plantar Fasciitis
Understanding the causes of plantar fasciitis is crucial in its prevention and management. Several factors can contribute to the development of this condition:
- Overuse: Repeated stress on the plantar fascia, often due to activities like running or standing for extended periods, can lead to micro-tears in the tissue, causing inflammation and pain.
- Improper Footwear: Wearing shoes with inadequate arch support or poorly cushioned soles can strain the plantar fascia and increase the risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
- Obesity: Excess weight places added stress on the feet, increasing the likelihood of inflammation in the plantar fascia.
- Age: Plantar fasciitis is more common in individuals between the ages of 40 and 60, as the plantar fascia tends to lose elasticity over time.
- Foot Structure: People with flat feet, high arches, or abnormal walking patterns are at a higher risk of developing this condition.
Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
Recognizing the symptoms of plantar fasciitis is essential for early diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Heel Pain: The most noticeable symptom is intense pain in the heel, typically felt during the first steps in the morning or after prolonged periods of rest.
- Arch Pain: Some individuals may experience pain in the arch of the foot, often described as a burning or stabbing sensation.
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the foot, especially after sitting for a while, is a common symptom of plantar fasciitis.
- Pain that Worsens with Activity: The pain may intensify with physical activities but may subside as the foot warms up.
- Swelling: Inflammation of the plantar fascia can lead to swelling in the affected area.
Diagnosis of Plantar Fasciitis
If you suspect you have plantar fasciitis, it’s essential to seek a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional. Diagnosis typically involves the following steps:
- Physical Examination: Your healthcare provider will perform a physical examination of your foot to assess your pain points and range of motion.
- Medical History: You will be asked about your medical history, including any recent injuries or activities that may have contributed to your symptoms.
- Imaging Tests: In some cases, imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs may be ordered to rule out other possible causes of your symptoms, such as stress fractures or heel spurs.
Treatment and Prevention
The good news is that plantar fasciitis is treatable, and most individuals can find relief through conservative measures. Here are some treatment and prevention strategies:
- Rest: Give your feet a break by reducing or avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain.
- Ice and Compression: Applying ice and using compression can help reduce inflammation and alleviate discomfort.
- Stretching Exercises: Incorporate daily stretching exercises to improve the flexibility of your calf muscles and Achilles tendon.
- Supportive Footwear: Invest in shoes with proper arch support and cushioning to reduce strain on the plantar fascia.
- Orthotic Inserts: Custom or over-the-counter orthotic inserts can provide additional support and alignment for your feet.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can teach you specific exercises and techniques to alleviate pain and improve foot function.
- Medications: In some cases, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to manage pain and inflammation.
Conclusion
Plantar fasciitis is a common and often painful foot condition that can affect anyone. By understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and seeking proper diagnosis and treatment, you can effectively manage and even prevent this condition. Remember that early intervention is key to a quicker and more comfortable recovery. Visit Critics Rant if you need more information or have any questions about plantar fasciitis.